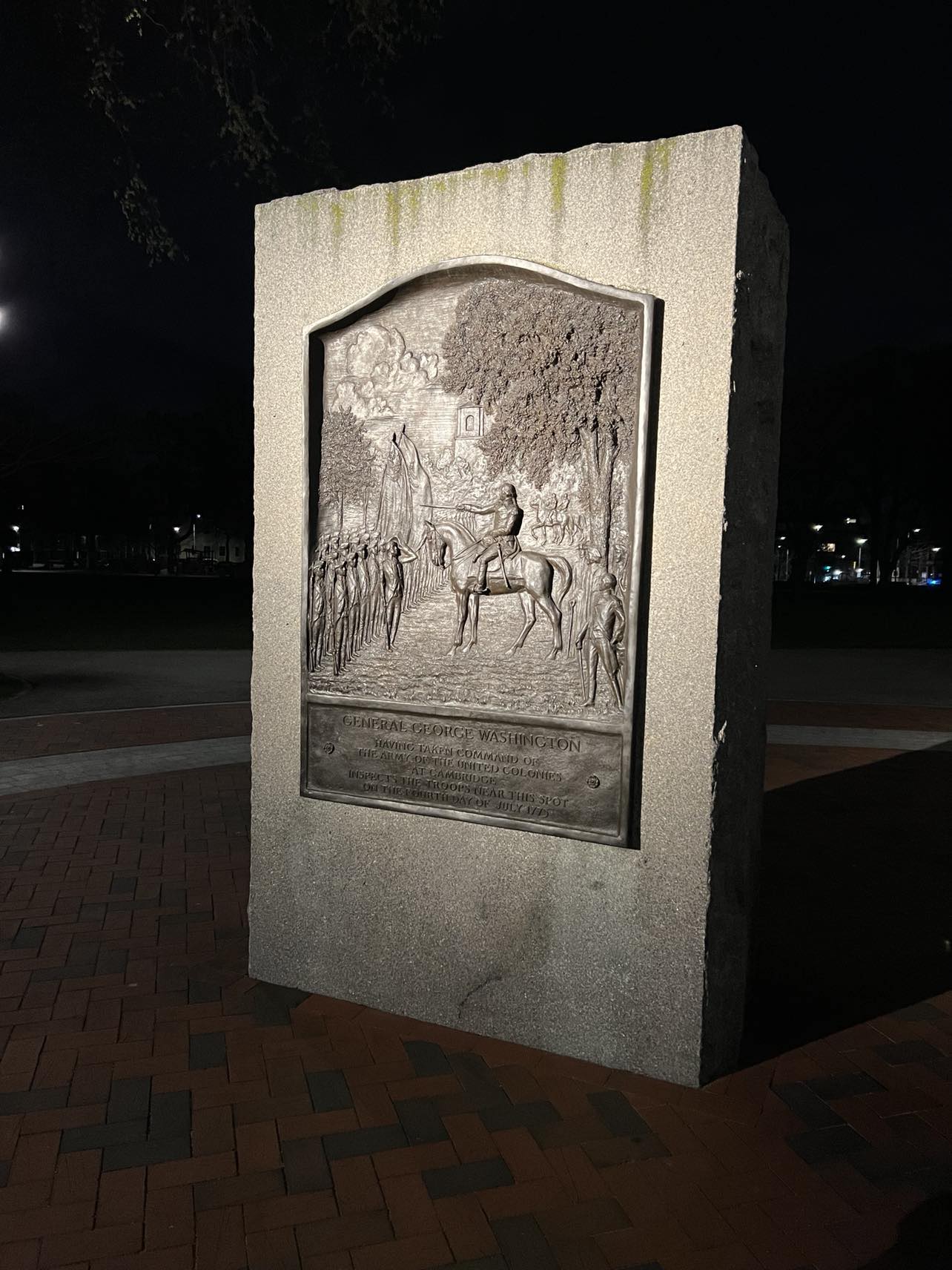
On July 3, 1775 George Washington formally took command of the Continental Army in Cambridge, Massachusetts. Appointed Commander-in-Chief by the Second Continental Congress on June 15, 1775, Washington arrived in Cambridge on July 3, 1775 and assumed command of a disorganized and poorly supplied force besieging British troops in Boston. His leadership would begin the transformation of colonial militias into a unified fighting force capable of challenging British military power.
Washington’s assumption of command occurred at a time when the American colonies were transitioning from protest to open rebellion. The battles of Lexington and Concord in April 1775 had already ignited armed conflict, and the Battle of Bunker Hill in June had demonstrated that colonial forces could stand up to British regulars, though at great cost. Washington understood the gravity of his new role. In a letter to the President of Congress, he wrote humbly, “I am truly sensible of the high Honor done me in this Appointment… I do not think myself equal to the Command I am honored with.” This characteristic modesty was paired with a strong sense of duty and resolve.
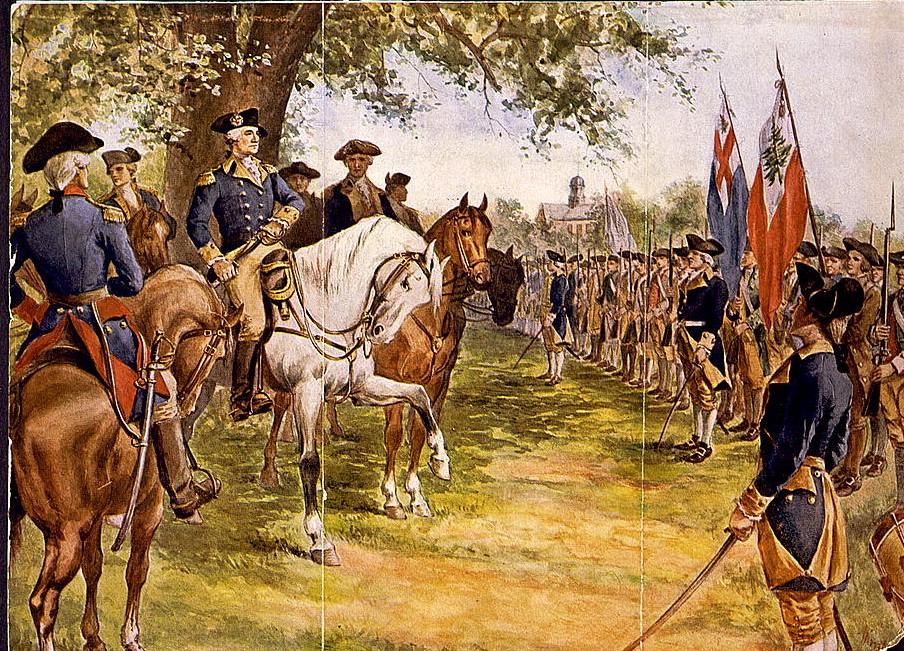
On July 3, Washington appeared before his troops on Cambridge Common, dressed in a blue coat with buff facings, signifying his Virginian roots. There is no official transcript of a speech he may have delivered that day, but contemporary accounts describe a solemn and determined atmosphere. One observer, Reverend William Emerson, noted in his diary, “General Washington… is a tall and noble-looking man, commanding the respect of all who see him.”
Washington immediately set to work imposing discipline, organizing supply chains, and creating a chain of command. Though former commander of the army, Major General Artemus Ward, worked hard on instilling discipline, he was not a man that instilled a lot of confidence. Washington was appalled by the state of the army, writing in frustration to Congress: “The Army… is in a very improper condition to carry on a vigorous War.” He introduced regular drills, uniform codes, and standardized procedures, striving to turn the disparate bands of militiamen into a functioning army. As historian David McCullough noted, “It was Washington’s presence alone that gave the army cohesion.”
Despite his military inexperience—Washington never commanded an army of this size—he brought a unifying vision and moral authority. His appointment was also politically astute, bridging the regional divide between New England and the southern colonies. A Virginian leading New England troops sent a clear message of unity in the face of British oppression.

The Cambridge encampment remained Washington’s headquarters until March 1776, when he successfully forced the British evacuation of Boston by fortifying Dorchester Heights with cannons brought from Fort Ticonderoga. This early strategic victory, achieved without major bloodshed, was a major morale boost and affirmed Congress’s faith in their commander.
In retrospect, July 3, 1775, was the beginning of an enduring legacy of leadership and a love of Washington by his men and officers. Through discipline, vision, and personal integrity, he began shaping a ragtag collection of volunteers into the Continental Army, laying the groundwork for American independence.

