The city of Boston, Massachusetts is steeped in American Revolutionary War history. The city has designed an entire trail–the “Freedom Trail”–a footpath that leads interested visitors around the city to the areas of most importance.
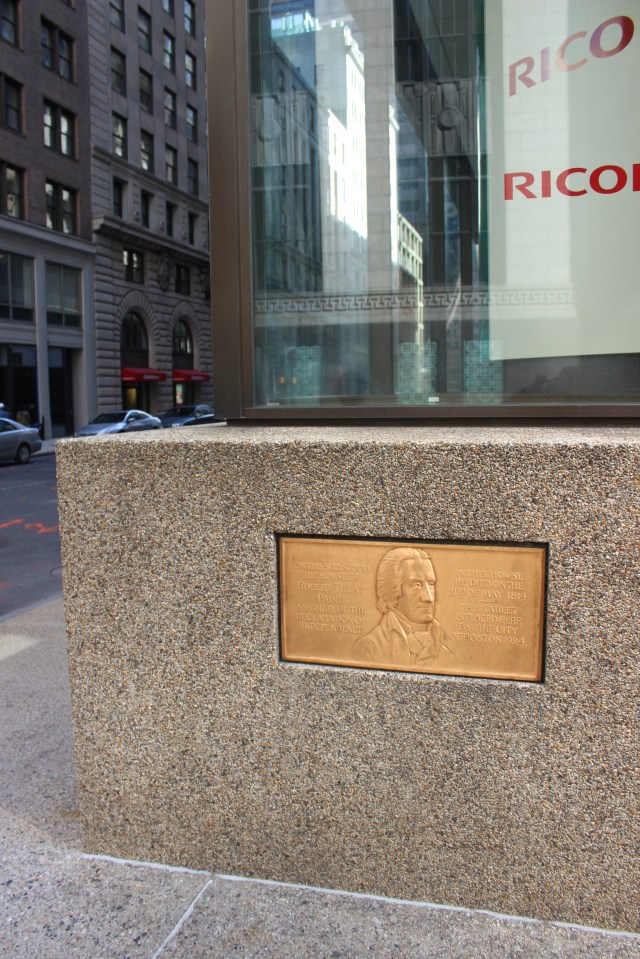
Yet, some history, is just, literally, stuck right on the walls of Boston. On the side of a modern office building, is situated the plaque below:

One of the 56 men that affixed his signature to the Declaration of Independence, Paine was born in Boston on March 11, 1731 and was actually given a middle name, a family tribute. His family legacy was well-established in the colonies and Paine himself was counted as an early advocate for the patriotic cause.
Yet, like the more famous John Adams, Paine also was a lawyer and dedicated to the law and order. He was the second attorney, along with the aforementioned Adams, to represent the British soldiers in the “Boston Massacre” trial. He continued to hope for reconciliation, hoping when he ventured to the Second Continental Congress, that the resolve of the colonies would bring the British Parliament to negotiate. On that same vein, Paine also put his signature on the Olive Branch Petition–the final attempt by the colonies to reach King George III and give their side of the story. When the king outright rejected the petition and did not even lay eyes on the document, Paine saw there was no hope and firmly planted himself in the camp of those clamoring for independence.
He became a vocal and valuable member of the Continental Congress and signed the Declaration of Independence on August 2, 1776. Returning to Massachusetts near the end of 1776, he became the Speaker of the Massachusetts House of Representatives the following year. In 1780 he was a member of the committee that drafted the state constitution and as attorney general he prosecuted members of Shays’ Rebellion in 1787.
His last public role was a justice of the Massachusetts Supreme Court from 1790 until his retirement in 1804. He was 83 years old when he died in the house that the plaque mentions. He was buried in the Granary Burying Ground in his native Boston, Massachusetts.
Another great patriot of the American cause, whose last house where his last days were spent, has a lasting memorial for those to discover. So, many historical treasures are just hanging there, waiting to be discovered in Boston.