Following the initial skirmishes at Lexington and Concord on April 19, 1775, colonial militias from throughout New England converged around Boston, with the area of Cambridge and Roxbury serving as the epicenters of the camps. These New England militia effectively layed siege to the city where British General Thomas Gage concentrated after April 19th. The British, cut off from the countryside, relied heavily on supplies brought in by sea. At the same time, American forces were eager to secure resources and deny the British any additional supplies from nearby coastal areas.
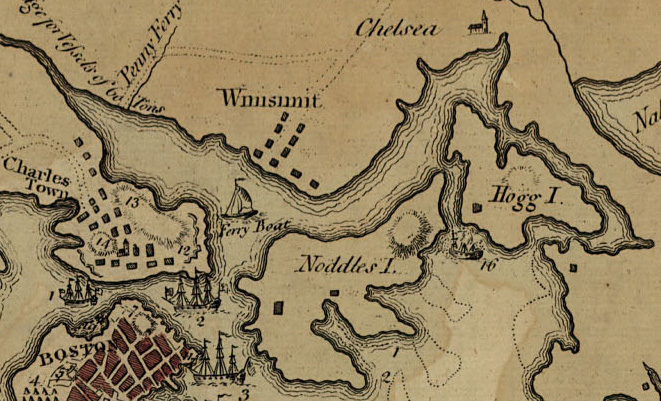
One such resource-rich area was Noddle’s Island and Hog Island both located in Boston Harbor. These islands contained valuable livestock and hay, which the British had been attempting to secure to feed their troops and horses. American intelligence reported that the British were planning to remove these resources, prompting a proactive operation by the colonial forces to beat them to it.
In early May, Dr. Joseph Warren led a group inspecting the islands and recognized their imporance. As part of the Massachusetts Committee of Safety, Warren led the effort for a reslolution to be passed to either capture or destroy the supplies on the islands. On May 14th, the Committee stated “Resolved, as their opinion, that all the live stock be taken from Noddle’s Island and Hog Island, and from that part of Chelsea near the sea coast, and be driven back; and that the execution of this business be committed to the selectmen of the towns of Medford, Malden, Chelsea, and Lynn, and that they be supplied with such a number of men, as they shall need, from the regiments now at Medford.” Soon the commander of the New England army around Boston, General Artemas Ward, put a plan in motion to quickly strike both islands.
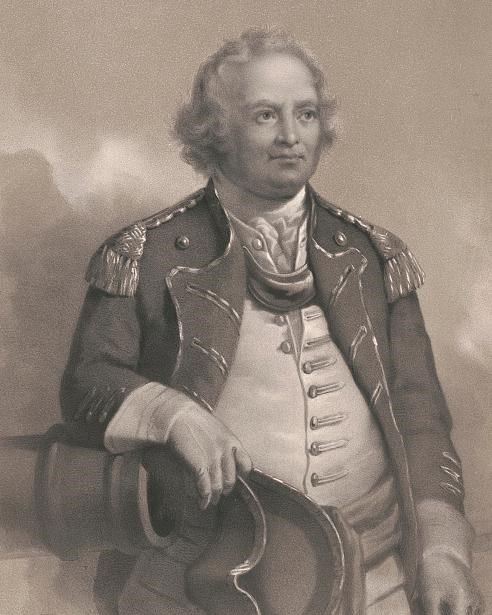
The American expedition was led by Colonel John Stark and Colonel Israel Putnam, both future generals in the Continental Army. The colonial forces, primarily composed of New Hampshire and Massachusetts militias, planned a nighttime amphibious raid to remove the livestock and destroy hay supplies that might benefit the British. On the night of May 27, colonial forces quietly moved onto Hog Island and began driving off livestock and burning haystacks. British forces, stationed in Boston and alerted to the colonial activity, responded by dispatching marines and the British schooner HMS Diana, a lightly armed but maneuverable vessel well-suited for operations in the shallow waters of the harbor.
As the colonists worked to transport livestock to the mainland, they encountered resistance from British marines who had landed on Noddle’s Island and began advancing toward their position. A sharp skirmish ensued, during which the American militia used the terrain to their advantage, fighting from behind trees, stone walls, and other natural cover. The colonial forces managed to repel the British marines, inflicting casualties and forcing a retreat.
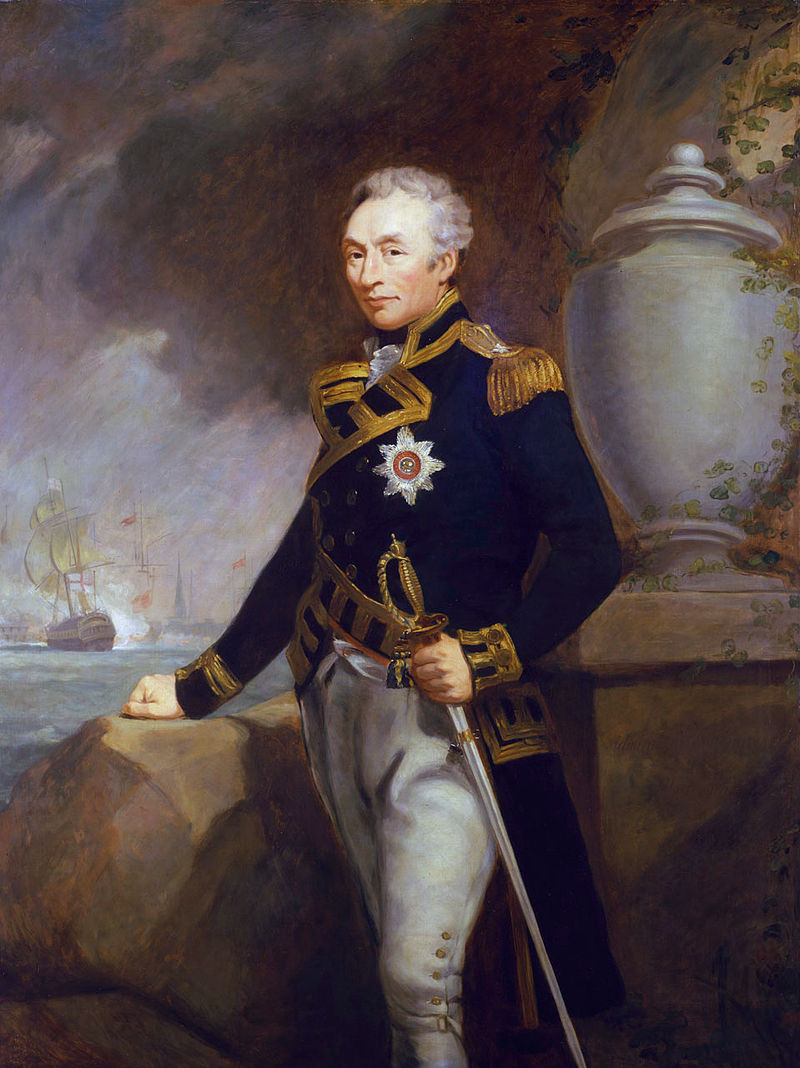

The turning point of the engagement came with the involvement of the HMS Diana. The schooner attempted to support the marines by moving up the narrow Chelsea Creek to engage the colonial militia and cut off their withdrawal. However, as the tide receded and the ship ventured too far inland, it became grounded in the shallow, muddy waters.
Seeing an opportunity, the colonists brought up field artillery from shore and opened fire on the stranded vessel. Over the course of the battle, they subjected the Diana to intense musket and cannon fire. Unable to refloat the ship due to the falling tide and increasing colonial pressure, the British crew was forced to abandon it. American forces quickly boarded the vessel, stripped it of usable supplies, weaponry and its 76 foot mast, and then set it ablaze, destroying the schooner completely.
The Battle of Chelsea Creek resulted in a clear American victory, both strategically and psychologically. The destruction of the HMS Diana marked the first loss of a Royal Navy vessel in the Revolutionary War, dealing a symbolic blow to British morale. For the colonists, it was a tangible demonstration of their ability to challenge British authority not only on land but at sea.

on Chelsea Creek “I wish we could have
something of this kind to do every day,”
Tactically, the victory helped to solidify American control of the Boston-area islands and limited the British army’s ability to forage for supplies. This contributed to the worsening conditions inside besieged Boston and increased pressure on General Gage. The morale boost for the colonial militias was significant; it reinforced the notion that British troops and naval forces were not invincible and that well-coordinated militia operations could succeed.
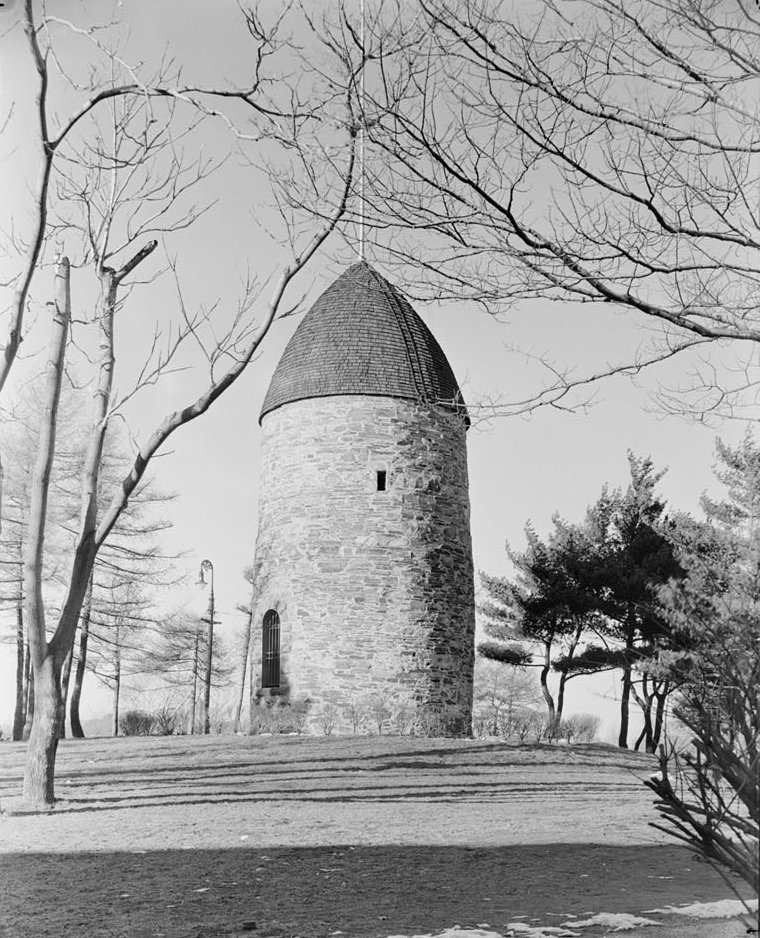
In addition, the battle was notable for showcasing early instances of American military ingenuity and leadership. Figures like Israel Putnam and John Stark went on to distinguish themselves in later battles, and the ability of the militia to effectively coordinate a land-sea operation foreshadowed the more sophisticated tactics that would develop over the course of the war. A few months later on August 1st, the mast of the HMS Diana was raised on Prospect Hill as a liberty pole. A symbol that was seen by not just the Americans around Cambridge but also the British in Boston. This location was also where legend states that George Washington ordered the first American flag, the Grand Union, to be raised on January 1, 1776.
While over shadowed by Lexington, Concord, or Bunker Hill, the Battle of Chelsea Creek played a crucial role in the early war. It helped secure the outer perimeter of the Siege of Boston, denied the British critical supplies, and emboldened the colonial cause at a time when confidence was still fragile. The success of the operation, including the destruction of the Diana, offered a dramatic image of colonial resistance and ingenuity that resonated beyond New England.
Today, the location of Noddle’s and Hog Island are gone. Nineteenth century and modern infill has completely reshaped the area from mudflats and tidal marshes to buildable land. Modern day East Boston, Winthrop and Logan Airport cover the area. The community of Somerville contines to commemorate the raising of the Grand Union flag on January 1 Diana‘s mast with a flag raising ceremony. Though mostly forgotten, the fighting along Chelsea Creek continued to embolden men like Joseph Warren and Israel Putnam and encourage their agressiveness a few weeks later on the Charlestown peninsula.



