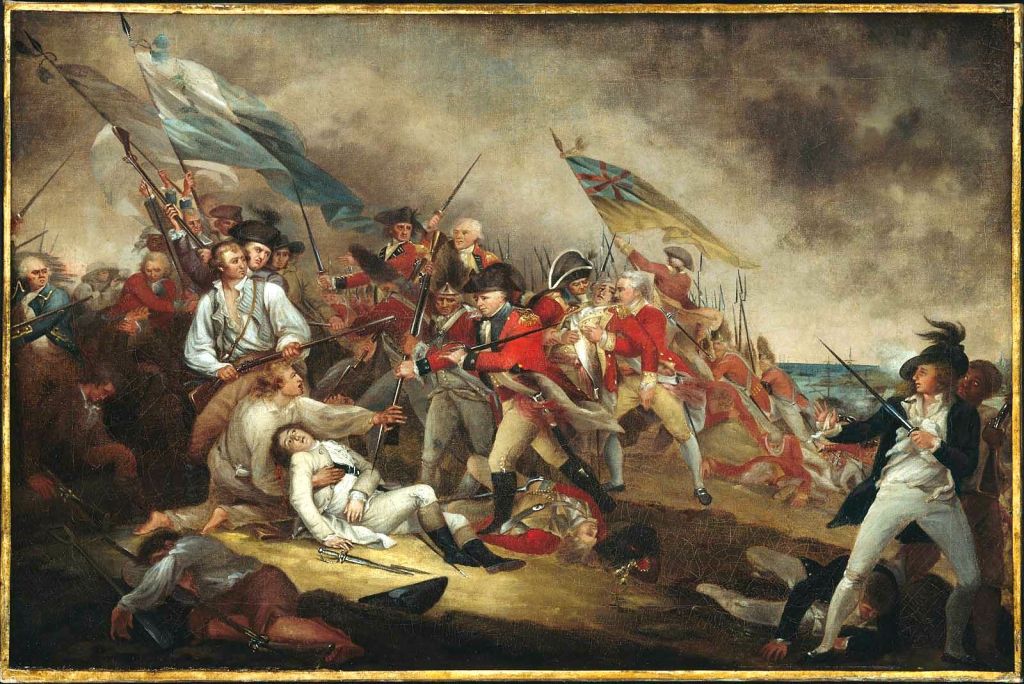
Emerging Revolutionary War welcomes guest historian Avellina Balestri
My American Revolution historical fiction trilogy, “All Ye That Pass By,” is thematically centered upon the pros and cons of oath-taking. Although the topic has been very much on my mind during the researching and writing process, I think many people who engage with the American Revolution on a popular level forget about the profound moral quandary of making
and breaking solemn declarations before God and Man.
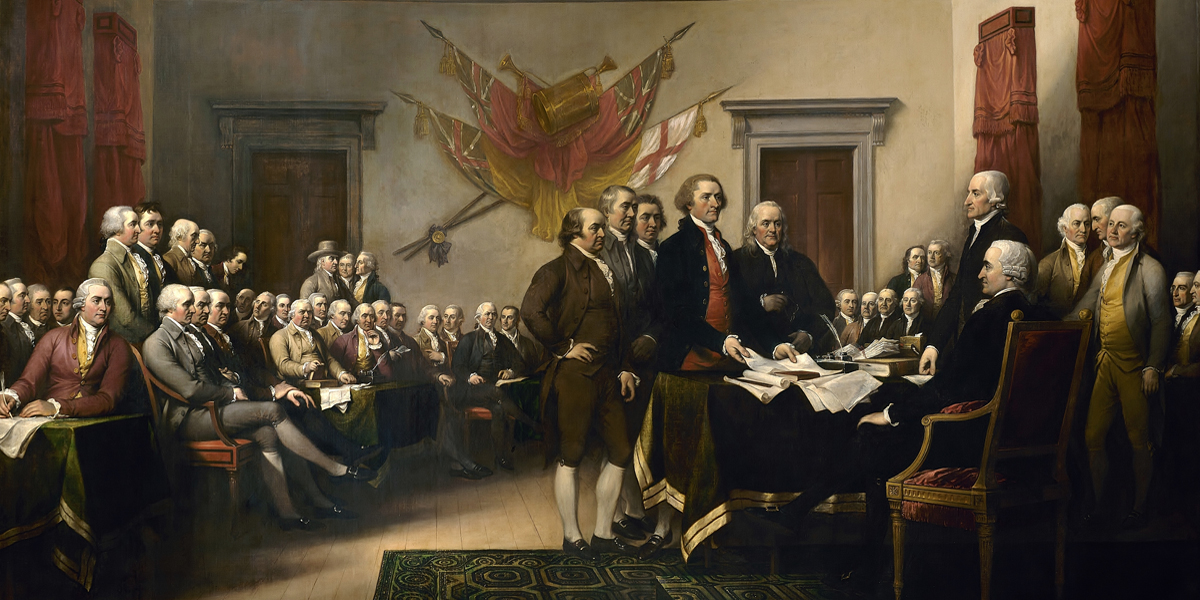

When the signers of the Declaration of Independence pledged their “lives, fortunes, and sacred honor” to the cause of rebellion, there could not help but be an element of contradiction, for they
were committing an act of treason against the King to whom they had previously sworn fealty. Too often we reduce this decision to a test of courage, necessary to take the risks and face the consequences that accompany defying one’s sovereign. We get a certain thrill from the idea of
defiance because it fits a certain popularized narrative framework. But perhaps this is partly because we have forgotten the rubrics of more religious ages in which hierarchies represented divine realities that dignified mankind.
Swearing oaths to kings and queens was a grave matter in both a spiritual and interpersonal sense. Most oath-taking rituals involved placing one’s hand (and often lips) upon the Cross on the Holy Bible, the symbol of salvation, and in the old rendering of such vows, wishing that one’s heart be cut out if proven false to the liege lord or lady, who would henceforth be held higher than family ties or even one’s own life. Calling down the heart-cutting curse was both a literal reference to execution and a symbolic statement of self-destruction, for what was a man’s heart if his word was worthless to the one you had sworn to defend by your life or death?
By contrast, unwavering zeal for one’s royal master may lead to one’s early demise, but that is not merely tolerable, but glorious, indeed, the most glorious hour of one’s life (as Major John Andre declared before minutes before his own life was taken), because it proved the depths of
one’s ability to be a good and faithful servant, and what is a man without a lord to serve? What
liberty can a knight enjoy if he will not swear his sword and be chained? These perennial
questions hearken back to the Anglo-Saxon epic of the Men of Maldon, who preferred death to
abandoning their lord, even as he lay slain by Norsemen upon the field. It is no small irony that
one of Maldon’s other famous sons was General Horatio Gates, whose trajectory runs in quite a
different direction.
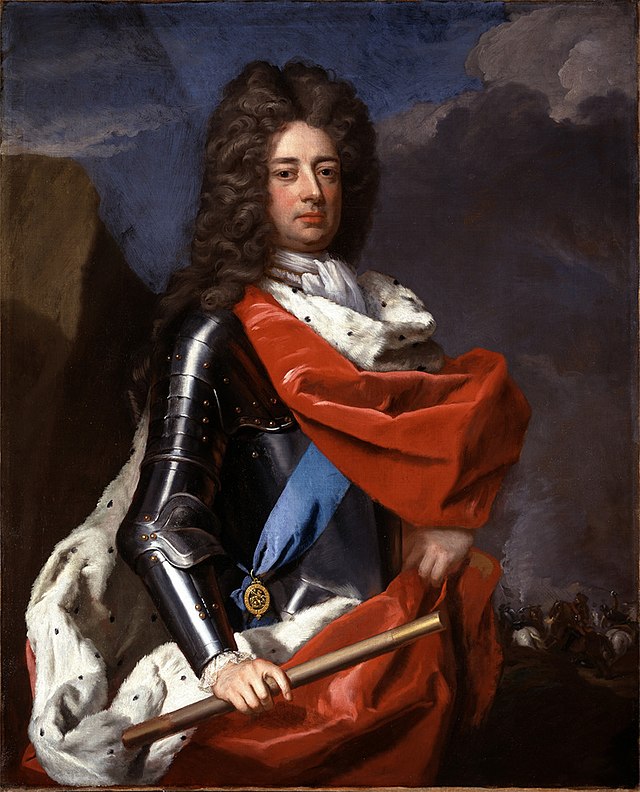

On that note, it is worth turning to the various figures in the long history of the British Isles and her overflowing empire who chose to break their oaths to reigning sovereigns by way of rebellion, from Lord Brooke (who fought in The English Civil War against Charles I), to the
Duke of Marlborough (who took part in The Glorious Revolution against James II), to Lord Murray (who fought in The Second Jacobite Rebellion against George II). To justify themselves under God and before Man, they usually appealed exception clauses based on a higher religious
obligation or a superior royal claim. For Brooke and Marlborough, it was because the kings were leaning too Catholic for their Protestant convictions; for Murray, it was because the Stuarts were the rightful rulers, unlawfully sent into exile.
Even in these cases, however, there is a sense that the participants never fully managed to
escape the shadow over their broken oaths. Yes, they might appeal to those “rare cases” brought
forward by philosophers and theologians from Thomas Aquinas to Samuel Rutherford, but they
had still committed what Dante deemed the most mortal of sins in the depths of his inferno.
Bearing that weight is exhausting for any mortal man, doomed to make constant self-defenses
while knowing the world will never truly trust them again. It is, in effect, to be branded by the
mark of Caine, for one who breaks his oaths has murdered the worth of his own word, a nearer
thing than even his own brother.
Jumping forward in time, the American Revolution is a unique case in that it was not fundamentally grounded in either a doctrinal nor a dynastic dispute. One would have to squint
incredibly hard to make the arguments of either Aquinas or Rutherford translate neatly into a
stamp of approval for the American Revolution. This is not to say the revolutionaries did not
borrow from the rhetoric of past uprisings, especially regarding the curbing of royal prerogative
(albeit colonial complaints were more directed at Parliament than at the King, even though the
King upheld his Parliament). But humanistic philosophies that flourished during the
Enlightenment introduced rubrics for revolution based on the will of the people. This, in turn,
started the domino effect that established the modern consensus of Democracy being inherently
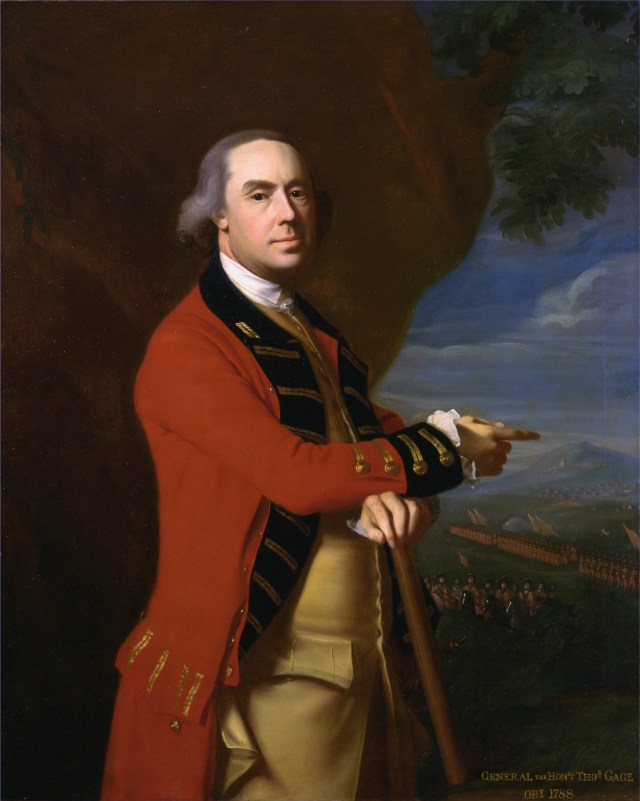
positive, even though General Thomas Gage’s warning about the effects of “democratic
despotism” is perhaps more relevant than we wish to admit.
Coming back to my own literary exploration, I strive to cast a particular light upon the experiences of Catholic recusants in the British Isles and North America from the 16th-18th centuries, who found themselves between a rock and a hard place in terms of oath-taking. This was especially the case for English Catholics of prominent lineage, who were forced to pay taxes
and tithes for refusing to conform to the Anglican Church, leaving their resources drained and their status diminished. By the latter part of the 18th century, following multiple failed Jacobite risings in favor of Catholic claimants, most were eager to dispel accusations of cowardice at best
and treason at worst for the old faith they keep against the odds. Even the pope acknowledged the House of Hanover by 1766. But in order to participate fully in British society, it was mandatory to take the Test Act, an oath acknowledging the King as Governor of the Church in England, a claim inherently repugnant to Catholic consciences.
Some resisted this temptation; others yielded to it. One of the most famous cases of apostasy in the period pertains to General Gage’s father and his father’s cousin, both coming from a staunchly Catholic lineage, who took the Test Act ostensibly to save their racing horses from being confiscated. That was the tip of the iceberg, of course; Catholics were not only forbidden from owning horses, but also bearing arms, voting, holding most offices, attending universities, serving in the military, and much more.
The decision to conform to the religion of the state often haunted those who made it. Oaths were understood religiously by society as whole, but for noble families there was a particular weight involved, since the Test Act was a successor of ancient chivalric vows taken by their ancestors. By taking it, Catholics would have sworn their souls to something which they believed put them in a state of mortal sin. Yet…would not breaking that oath be a mortal sin too?

In this quandary, whatever they did would be a slap in the face to saints and martyrs most highly praised in their tradition, such as Thomas More and Edmund Campion, who preferred to die rather than sign the Oath of Supremacy. Nevertheless, they met their fates praying for the King and Queen who killed them, embodying fidelity under fire. Another case honored by the oppressed Catholic community was Lord Derwentwater, who rose up in the first Jacobite Rebellion of 1715, and preferred beheading to either recanting his faith or swearing an oath to the House of Hanover which he deemed to be illegitimate. Interestingly, it was said Derwentwater’s heart remained incorrupt, in counteraction to the curse of having it cut out.
Again, we see the crushing effects of previous failed rebellions, and cannot help but compare
them to the effects of the American Revolution. The rebellion, predicted to be a flash in the pan
by the British establishment, proves more successful than most imagined, shattering old
structures in a manner which some will find terrifying and others liberating. In this new world,
many hope to enjoy a chance to start over with a clean slate. But for those who have taken the
Test Act, going down such a path would require trekking into uncharted territory, calling into
question every aspect of loyalty and identity, on earth as it is in heaven. Embracing the
revolutionary cause would inherently be a process of unbecoming, shedding one’s understanding
of past obligations and hoping the gamble would pay in the end.
For Catholic recusants, the experiences of Charles Carroll of Carrollton served as an example of what might be possible in America. His claim was that King George is a traitor to them rather than them being a traitor to him, and that having been placed under religious suppression, his fellow Catholics had the right to seek alternative options for their own betterment as a community of faith. The outcome of the revolution might have been a risk, but he had proven that it was already disrupting the old order and causing the disabilities placed upon Catholics to crumble. Prejudice might remain, but Carroll has already overcome various civil obstacles against his faith in Maryland, the one-time Catholic colony laid low, and George Washington, commander-in-chief of the Continental Army, who once took the Test Act himself, had demonstrated his willingness to uphold religious toleration in his army.
And yet…the question of an oath’s weight still bore down on those confronted with such a choice, raised with the conviction that even an oath with questionable aspects was considered worthy of adhering to “as far as the law of God allows.” The way in which each man and woman wrestled with their conscience when it came to such heavy matters was as complex and fascinating as the war itself, and my experience of bringing that inner conflict to life as a writer has been one of the most rewarding aspects of the creative process.
Avellina Balestri is a Catholic author and editor based in the historic borderlands of Maryland and Pennsylvania. She represented the state of Maryland at The Sons of the American Revolution National Orations Contest and is the author of the American Revolution historical fiction trilogy “All Ye That Pass By,” the first installment of which, “Gone for a Soldier,” is available on Amazon. Avellina is also the Editor-in-Chief of Fellowship & Fairydust, a magazine inspiring faith & creativity and exploring the arts through a spiritual lens.
For more information about the author and her various projects, please visit the following websites: