Join us this Sunday, January 11th at 7pm as we welcome back historian Patrick Hannum as we discuss the events in Virginia after the Battle of Great Bridge. The results of the British loss at Great Bridge had profound impacts on Dunmore’s plans in Virginia which led to the destruction of Virginia’s largest city. Was Norfolk burned by Dunmore as has been popularly understood or is the story more complicated? What became of the former slaves that joined Dunmore’s army? Tune in and learn about the events in Virginia in the winter 1775 – spring 1776. This Revelry is pre-recorded and will be posted to our Facebook page on Jan. 11 at 7pm and also to our You Tube and Spotify channels.
Tag: Virginia
Was the Battle of Point Pleasant the First Battle of the Revolution?
Emerging Revolutionary War welcomes back guest historian Evan Portman
By the time Ralph Waldo Emerson immortalized the “shot heard round the world” in his 1836 “Concord Hymn”, the battles of Lexington and Concord had already achieved fame as the first engagement of the Revolutionary War. However, in the early twentieth century one West Virginia historian began to argue that the true “shot heard round the world” had occurred six months earlier on October 10, 1774, at the battle of Point Pleasant.

The battle was the culmination of Lord Dunmore’s War, a five-month campaign against the Shawnee and Mingo tribes in an effort to quell the violence along the Ohio frontier.[1] Virginia settlers had begun moving into the Ohio Country following the Treaty of Fort Stanwix, in which the Iroquois Confederacy ceded the territories of present-day Kentucky and West Virginia to the Colony of Virginia. However, the Shawnee had not been consulted regarding the treaty and claimed ancestral hunting rights to the region, responding with violent raids along the frontier to reclaim their land.[2] Virginia Colonial Governor John Murray, 4th Earl of Dunmore sanctioned the colonial militia to wage a campaign against the Native Americans after white settlers began reacting violently, themselves.[3]
Continue reading “Was the Battle of Point Pleasant the First Battle of the Revolution?”An Englishman’s Journal of the Revolutionary War: The Journals of Nicholas Cresswell 1774-1777
Emerging Revolutionary War welcomes guest historian Kenneth Bancroft
“Nothing but War is talked of…This cannot be redressing grievances, it is open rebellion…”1
250 years ago on October 20, 1775 a 25 year old Englishman wrote these words in Alexandria, Virginia, noting that “everything is in confusion…soon they will declare Independence.”2.Nicholas Cresswell had arrived in America a year and a half prior to that entry in a journal that he kept to chronicle his venture to “shape his course in the world” and set up a new life inVirginia, “as I like the situation of that Colony the best.”3 He was aware of grumblings from colonials, but his focus was on land and his adventure had him traveling and trading with the Native Americans in the Ohio country and experiencing the slave culture in the colonies, especially the horrific sugar plantations in Barbados.
But what his journal is most known for is his observations and critique of the revolutionary world from Virginia to New York in 1774 through 1777. Cresswell’s misfortune, among others, was that he arrived in America seeking opportunity just as the Imperial Crisis over the Intolerable Acts had began. News of, and reaction to the closure of the port of Boston frequently disrupted his schemes and social life. As an Englishman still loyal to the Crown, his Revolutionary War journal offers a unique outsider look at the costs of the conflict in the country and towns as opposed to the more common tomes of soldier life.
“No prospect of getting home this winter, as I am suspected of being a Spy.”4 Cresswell’s tenure in America was tenuous. Unsuccessful in trying to establish himself with land and basically broke, he blamed his misfortune on the “Liberty Mad”5 political climate that considered him a ‘Tory’ who would not commit to the cause. His penchant for getting into drunken political arguments did not help and kept getting him in trouble with local Committees of Safety.
“Am determined to make my escape the first opportunity.”6 By that point Cresswell knew it was time to forgo his quest and return to England, but the question was how, especially with non- importation measures and the war closing ports. What followed next for Cresswell was an amazing account of encounters with revolutionary notables and locations such as Thomas Jefferson, Patrick Henry, and British General Howe in Philadelphia, Williamsburg, and New York respectively. Ultimately, Cresswell was able to secure passage back to England where he reluctantly picked up where he left off by order of his father to “shear or bind corn.”7
1 Nicholas Cresswell, The Journals of Nicholas Cresswell, 1774-1777, (North Charleston, South Carolina: reprinted 2024), 97.
2 Ibid, 97.
3 Ibid, 3.
4 Ibid, 101.
5 Ibid, 47.
6 Ibid, 143.
7 Ibid, 214.
The Journals of Nicholas Cresswell was first published in 1924 and offers a candid account of the American Revolution from a viewpoint not typically explored. Its accounts of mustering militia, salt shortages, political pulpits, and anti-Tory riots and fights add color to our revolutionary origins. Add to that Cresswell’s experiences with the Native Americans in the Ohio country and the plantations in Barbados which further inform our understanding of our colonial past. Join Cresswell’s journey! To read more about Cresswell’s journey click here. The blog is an online platform and resource to follow his daily posts as they occurred 250 years ago. Keyword search features and research links are featured as well. Follow along on Facebook, too, at Nicholas Cresswell Journals.
Rev War Revelry: Dunmore and the Virginia Gunpowder Incident

Today marks the 250th anniversary of the Virginia Powder Alarm in Williamsburg, VA. To commemorate the anniversary, join us this Sunday, April 27th at 7pm on our Facebook page as we welcome ERW historians Rob Orrison, Mark Maloy with Maureen Wiese and J. Michael Moore to discuss the events leading up to the April 21, 1775 Powder Incident in Williamsburg, VA. A few days after Lexington and Concord (unknown to the Virginians at the time), Governor Lord Dunmore removed powder from the magazine in Williamsburg. This event led Patrick Henry to lead militia towards Williamsburg and possible standoff with the Governor. As news arrived on April 28 of the bloodshed outside of Boston, tensions rose even higher.
Join us as we discuss another 250th anniversary event that led to the beginning of the American Revolution. This podcast will be recorded and posted on our Facebook page on April 27th at 7pm. Then it will be posted to your You Tube and Spotify pages.
To learn more about the Virginia Powder Alarm and the events to commemorate the Alarm at Colonial Williamsburg, visit: https://www.colonialwilliamsburg.org/discover/historic-area/historic-places/magazine/the-gunpowder-incident/
Guest Book Review: Thomas Jefferson and the Virginia Statute for Religious Freedom: Faith & Liberty in Fredericksburg
Among America’s Founding Fathers, Thomas Jefferson is among the most well-known. Author of the Declaration of Independence, Governor of Virginia, Minister to France, and the third President of the United States, Jefferson’s public career is familiar to many Americans. Of his many accomplishments, his authorship of the Statute of Virginia for Religious Freedom is perhaps less well-known among the public, but was one of which he was supremely proud. In Thomas Jefferson and the Virginia Statute for Religious Freedom: Faith & Liberty in Fredericksburg, Michael Aubrecht expertly delivers the story of the creation of this remarkable document and its relationship to the city in which it was written.
The Virginia Statute for Religious Freedom was written in Fredericksburg, Virginia in January 1777. Jefferson and four other men had been appointed to a Committee of Revisors tasked to examine Virginia’s existing laws and redraft them as necessary for the newly independent Commonwealth. Jefferson’s Statute, originally known simply as Bill 82, was only one of more than a hundred bills cataloged by the committee, but its significance has certainly been profound. Aubrecht’s narrative goes beyond telling how Jefferson wrote the document, however. Indeed, historians are not sure as to when exactly that occurred during the week that the committee met at Weedon’s Tavern in Fredericksburg. Instead, Aubrecht expertly places the story of the document’s creation within the context of the time and place it was written.
Each of the book’s thirteen chapters is essentially a vignette, concisely covering the man who wrote the statute, his and the nascent country’s views towards religion and religious practice, and the city and tavern in which it was written. The author also covers topics related to statute’s legacy, including its commemoration, and civic organizations, such as the Jefferson Institute, that perpetuate that legacy. Thus, while the story of the writing of the Virginia Statute for Religious Freedom can be and, indeed has been, quickly and effectively described on interpretive signs and monuments, Aubrecht effectively focuses on the sentiments and character of the man and locations that shaped the document.
Thomas Jefferson was not a one dimensional figure and Aubrecht does not whitewash his chief character. Jefferson was a man with many virtues and talents, but also possessed his share of faults. Aubrecht, like many other historians of the Colonial and Early Republican eras, observes and notes the contradiction between Jefferson’s views on liberty and the fact that his way of life was entirely dependent on slavery. Such objectivity only serves to strengthen the credibility of Aubrecht’s work.
Aubrecht’s work is masterfully researched. As is the case with any effective work of history, the work is truly based on extensive primary source research, chiefly the papers and correspondence of Jefferson. Scholars examining topics relating to religion in Colonial and Early America will find value in mining Aubrecht’s bibliography. Michael Aubrecht’s Thomas Jefferson and the Virginia Statute for Religious Freedom: Faith & Liberty in Fredericksburg will be of interest to anyone interested in Early American history and is a must read for scholars researching religious attitudes during this fascinating and complex period.
Review by: Timothy Willging, Fredericksburg, Virginia.
“Fight and Be Strong” Battle of Point Pleasant October 10, 1774
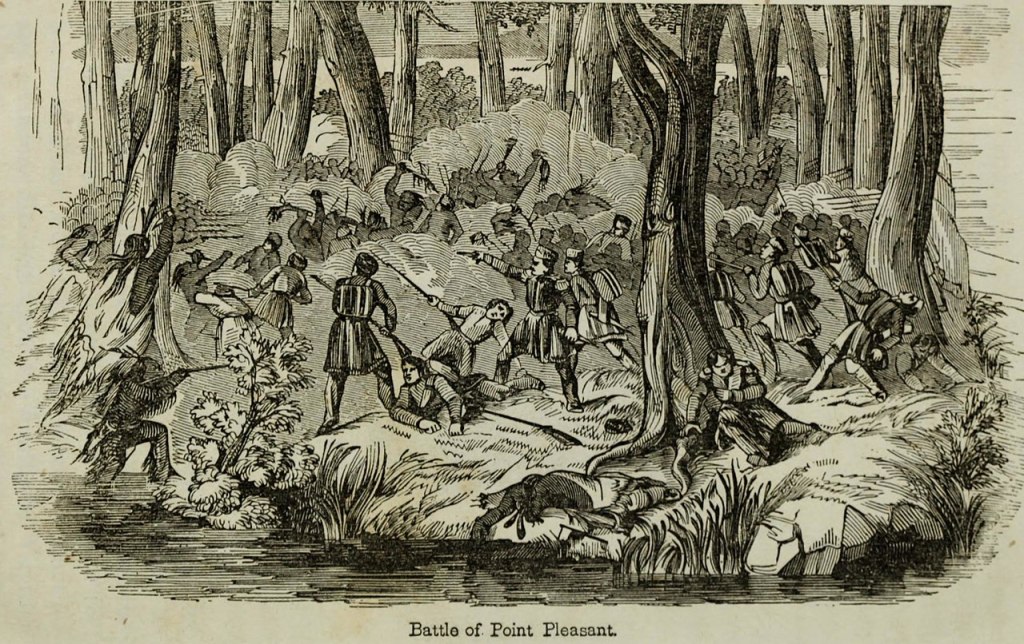
The ground fog was thick off the Ohio; the air was chilly on that early October morning. Two groups of hunters moved north along the river in the pre-dawn darkness, hoping to shoot a deer for their breakfast. Instead, they stumbled across something unexpected: Shawnee warriors! The battle of Point Pleasant was on.

In the summer of 1774, exactly 250 years ago and on the very eve of the American Revolution, the Virginia Colony went to war, but not with the British. In fact, the colonists at this stage still considered themselves to be British. Virginia went to war that summer against the Shawnee, Mingo, Wyandot, and other Native American tribal nations west of the Appalachian Mountains. As wars go, this wasn’t much of one, lasting barely six months and with only one decisive battle.
It stemmed from what one side called emigration and what the other considered encroachment. Bodies of English settlers, in ever increasing numbers, were crossing the mountains in hopes of settling land in the Ohio River Valley. This was territory that had been claimed by the French and transferred over to the British at the end of the Seven Year’s War. To the tribal nations in the Ohio Valley, like the powerful Shawnee, it was an affront. The settlers were looked upon as invaders, encroaching upon ancestral hunting grounds. Inevitably, the stage was set for violent and bloody clashes between these two peoples.
Hoping to pacify the frontier and establish once and for all Virginia’s jurisdiction over the Ohio Valley, the colony’s royal governor, John Murray, 4th Earl of Dunmore, asked the House of Burgesses to declare war and he called out the Virginia militia. In the years to come, many of the men serving in these militia companies would go on to distinguish themselves as officers and soldiers in the Continental army during the Revolution. For them, the fighting on Virginia’s frontier, in what came to be called Dunmore’s War, would serve as a dress rehearsal. This would be the last time in our nation’s history that a colonial American militia would march to war under the banner of the British crown.

At the Treaty of Fort Stanwix in 1768, the Iroquois peoples of the powerful Six Nations sold lands south of the Ohio River to the British, from Fort Pitt (modern-day Pittsburgh) down to the Louisa River (now the Kentucky River). This was territory the Iroquois believed to be part of their domain. For money and gifts totaling around £10,000, the Six Nations ceded to the Crown lands making up the modern states of Kentucky and West Virginia. The Shawnee and other western tribes in the Ohio Valley were outraged as white hunters, surveyors, land agents and settlers began to pour over the mountains. A trade-off of terror began, with both sides viciously attacking the other.
In the late summer of 1773, the first planned emigration into the new territory of Kentucky was undertaken. A prominent leader of this enterprise was Captain William Russell, a substantial landowner in southwestern Virginia and a magistrate of the newly created Fincastle County. Another organizer and the man who would act as guide for this first emigration attempt, made up of his and several other families from the Yadkin River Valley in North Carolina, was an obscure hunter named Daniel Boone. Boone led a party of 50 men, women and children through Powell’s Valley in southwestern Virginia, hoping to pass through Cumberland Gap into Kentucky. On October 10, just three miles behind Boone’s main party, his 17-year-old son James, 17-year-old Henry Russell, and a small group of young men, bringing up cattle and other supplies, were attacked by 19 Shawnee, Cherokee, and Delaware warriors. Both Boone and Russell were shot and hideously tortured to death. Word of the attack spread, causing the elder Boone’s party to turn back, abandoning all hopes of settling in Kentucky.
In late April of 1774, at a white trading post on the south bank of the Ohio River called Baker’s Bottom, several peaceful men and women of the Mingo tribe were murdered and scalped by white settlers believed to be under the leadership of a man named Daniel Greathouse. Among the victims were family members of a Mingo leader named Talgayeeta; he was known to the English as John Logan. As a result of the attack, the once peaceful Logan swore vengeance and, accepting help from the Shawnee, began indiscriminately attacking isolated white farmsteads along the Monongahela River throughout the summer.

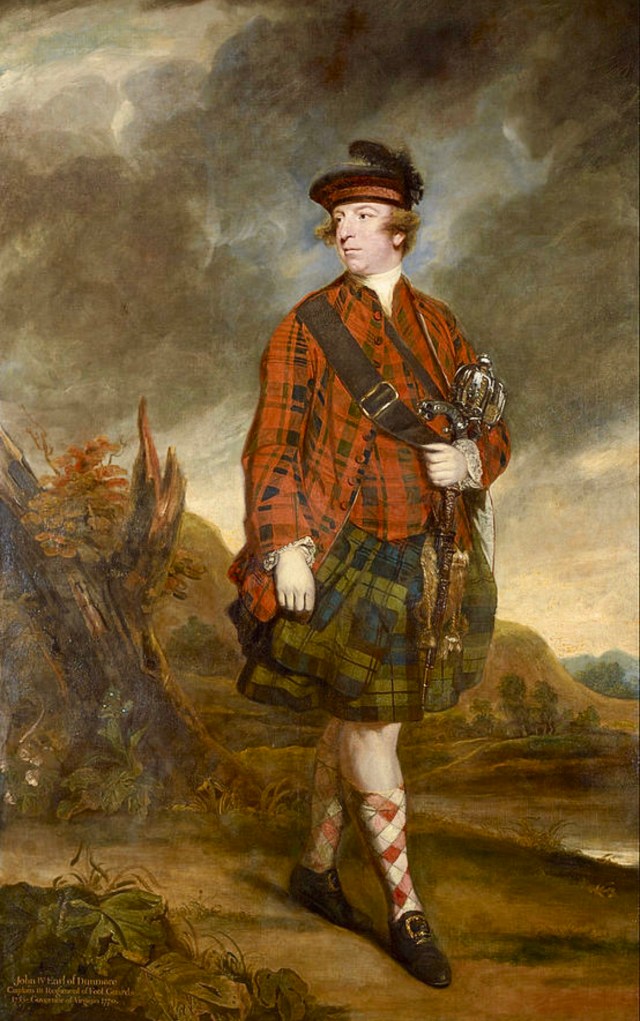
With word of the atrocities reaching Williamsburg, Governor Dunmore sent out a circular letter to all county lieutenants to be on the alert, build small forts and blockhouses for more security and to send out rangers to watch the trails. He was growing frustrated with the Virginia House of Burgesses for not creating regular, provincial military units to defend the frontier. The burgesses were preoccupied with the political unrest in the east, mainly due to parliamentary taxation. They passed a resolution to observe a day of humiliation, fasting, and prayer in response to the Boston Port Bill, which had resulted from the Boston Tea Party in December 1773. On May 26, Lord Dunmore dissolved the House of Burgesses and under his authority as royal governor, mobilized the Virginia Militia.
In late July came the first action of the militia. An expedition against an important Shawnee village on the Muskingum River, Wakatomika, was led by Major Angus McDonald. At Fort Fincastle, near modern-day Wheeling, WVA, McDonald’s battalion of 400 men pushed off in canoes and small boats on the Ohio River. Among his company commanders were two future Patriot leaders of the Revolutionary War, George Rogers Clark and Daniel Morgan. Combat with the Shawnee was minimal, although McDonald’s force did suffer some casualties. Wakatomika was plundered and burned, along with several other villages before the militiamen returned to Fort Fincastle. On the whole, the expedition had accomplished very little and, instead of curbing the Native American attacks on settlers, actually caused the attacks to increase. Lord Dunmore now knew that overwhelming force would be needed.
In the late summer of 1774, Dunmore authorized the creation of two divisions of his militia, north and south. At Winchester, he mustered around 700 men from Virginia’s eastern counties. The Governor was disappointed, however, to learn that his invitation to join the division, made to a retired British army officer living in Berkeley County, was turned down. He was Horatio Gates, future major general in the Continental army, victor at the battle of Saratoga in 1777, and the man who suffered a devastating loss to the British at Camden in August 1780.
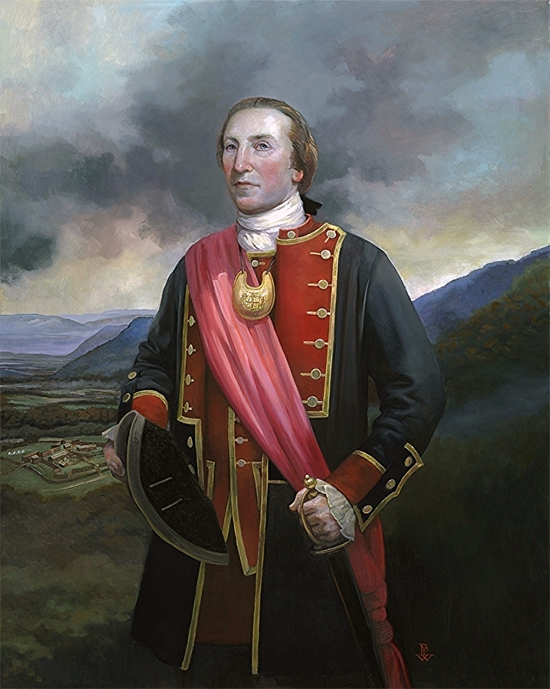
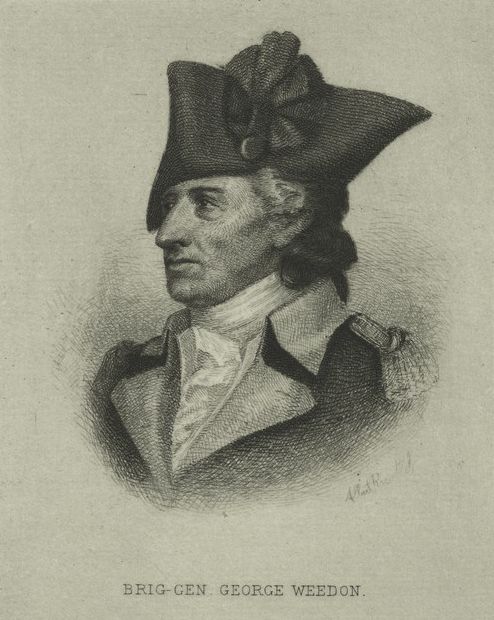
To the south, at Staunton, VA, militia Colonel Andrew Lewis, a future brigadier general during the Revolution, mustered ultimately around 1,100 men from the western counties of Augusta, Botetourt, Fincastle, Bedford, and Culpepper. With negotiations failing, by late August, Lord Dunmore put the Northern and Southern Divisions into motion. Their plan was to rendezvous on the Ohio River and march on the upper Shawnee villages on the Scioto River, in modern-day Ohio. Dunmore’s Northern Division marched west from Winchester to Fort Pitt, then down the Ohio to Fort Fincastle. There, 500 more men joined the division. Many of Dunmore’s troops had no weapons so he sent back to Williamsburg for 300 stands of arms. Dunmore’s second-in-command was Colonel Adam Stephen, another future major general in Washington’s Continental army. On October 2, the division moved farther south down the Ohio, to Fort Gower on Hockhocking Creek.
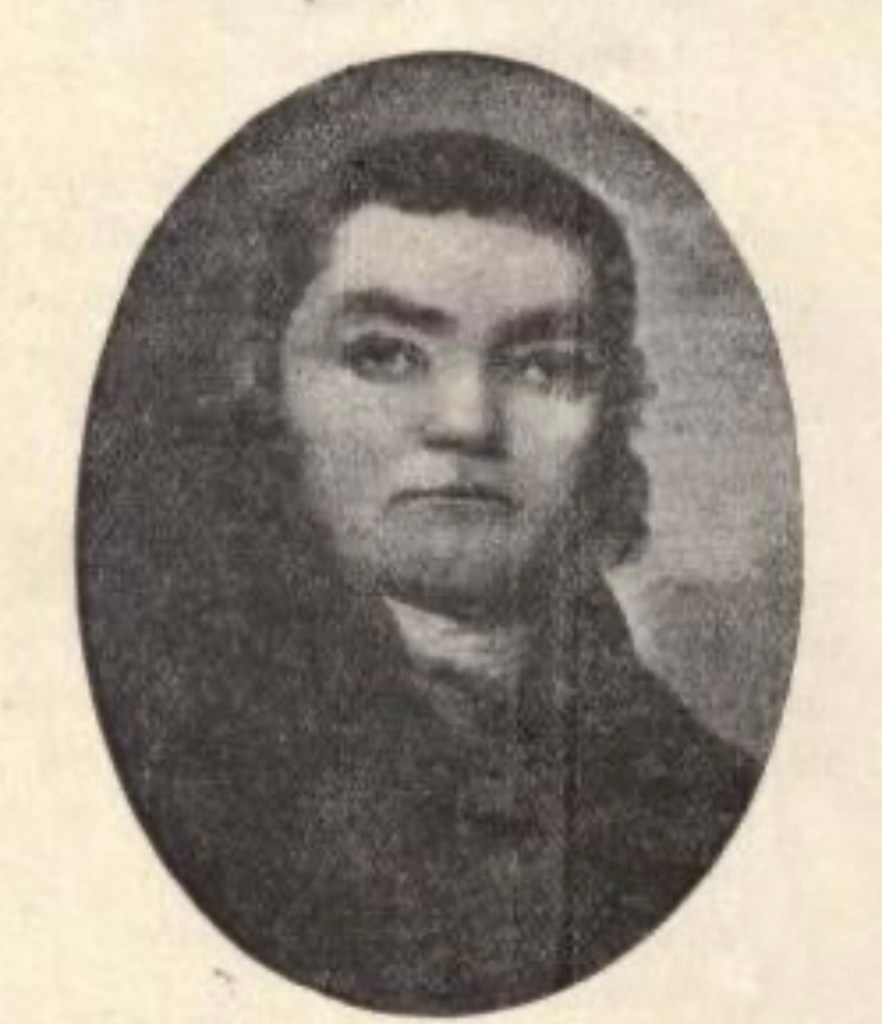

Colonel Andrew Lewis
From Staunton, Andrew Lewis marched his Southern Division west to a place called Great Levels, on the Greenbriar River. He named it Camp Union, on the site of modern-day Lewisburg, WVA. He then headed south, hitting the Kanawha River and following it west to where it empties into the Ohio at a place called Point Pleasant. Lewis’ lead elements arrived there on October 6 and began building barricades from the Ohio River on their left around to the Kanawha, which was at their backs. They also built pens and corrals for the livestock that would feed Lewis’ companies.
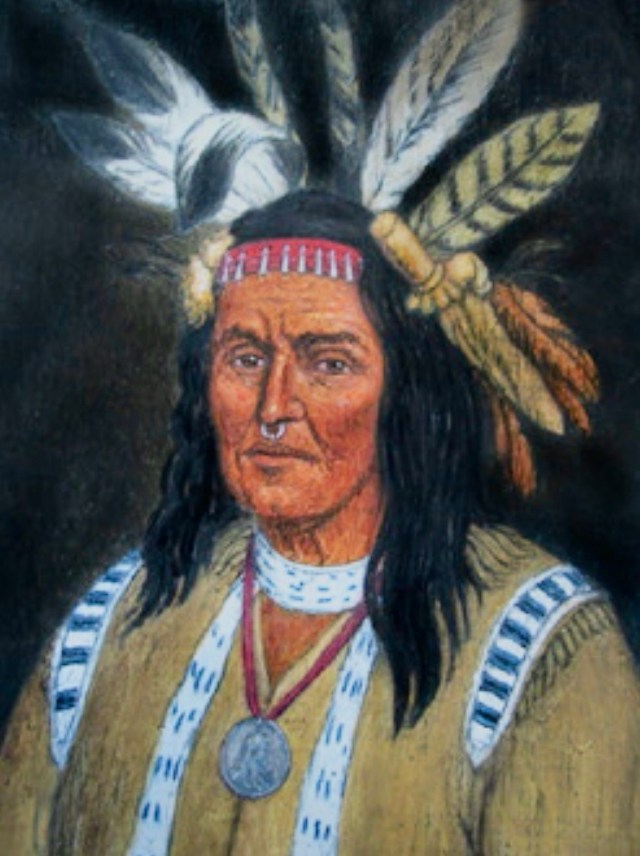
Leading the Shawnee and several other allied tribes as head war chief was a man named Hokoleskwa, also called Cornstalk. He commanded a force of around 1,000 warriors, which possibly included the future Shawnee war chief, Blue Jacket. Though his army was equal in size to both of the Virginia militia divisions individually, Cornstalk would be greatly outnumbered were those divisions to rendezvous, as planned. He decided, then, to attack each division separately and destroy them in detail. Being closer to the Southern Division, he chose to attack it first. On the night of October 9, Cornstalk rafted his army across the Ohio River at Old Town Creek, about five miles above Col. Lewis’ encampment. They then marched south to within two miles of the militia.

In camp, Lewis issued a rather unpopular order. Feeding his troops from the livestock he had brought along from Camp Union, Lewis ordered the oldest and poorest quality beeves butchered first. Not having a taste for stringy beef, two separate, two-man hunting parties set out before dawn on the foggy morning of October 10, moving north along different paths, looking for deer. After walking nearly two miles, both hunting parties stumbled upon Cornstalk’s warriors. Shots were fired and one of the hunters, Pvt. Joseph Hughey of Fincastle, was killed. The other three made their escape and brought news of the enemy presence back to Col. Lewis.
Thinking this was possibly a large scouting party, Lewis ordered two detachments of 150 men each to move up and reconnoiter. On the left, close to the Ohio River, were men from Botetourt County, commanded by Col. William Fleming. On the right, farther inland, were Augusta County militiamen commanded by Lewis’ own brother, Col. Charles Lewis. Around sunrise, Cornstalk’s warriors attacked, opening a brisk fire on the Virginians. Charles Lewis was hit almost immediately, in the abdomen. While being helped back to the encampment, he called to his men: “I am wounded, but go on and be brave.” Fleming’s Botetourt men also came under fire. The militiamen were outnumbered and the Shawnee attack was so fierce that both Virginia detachments faltered and were forced to fall back, ultimately around 200 yards. William Fleming was likewise hit, with wounds to the head and left arm. He continued to direct his men, though, until weakening from his wounds. Under his own power, he walked back to the encampment. A gap in the line separated the militia detachments. Warriors began rushing forward to exploit that breach. Directing the battle from the encampment, Andrew Lewis ordered Col. John Field of Culpepper forward with 200 men to assume command on the right, with orders to extend his left flank to link up with the Botetourt contingent. Lewis sent another 200 troops to join the Botetourt men, with orders for Captain Evan Shelby to assume command on the left. With more Virginia troops becoming engaged, Cornstalk’s initial superiority in manpower was starting to fade. The tide was turning.
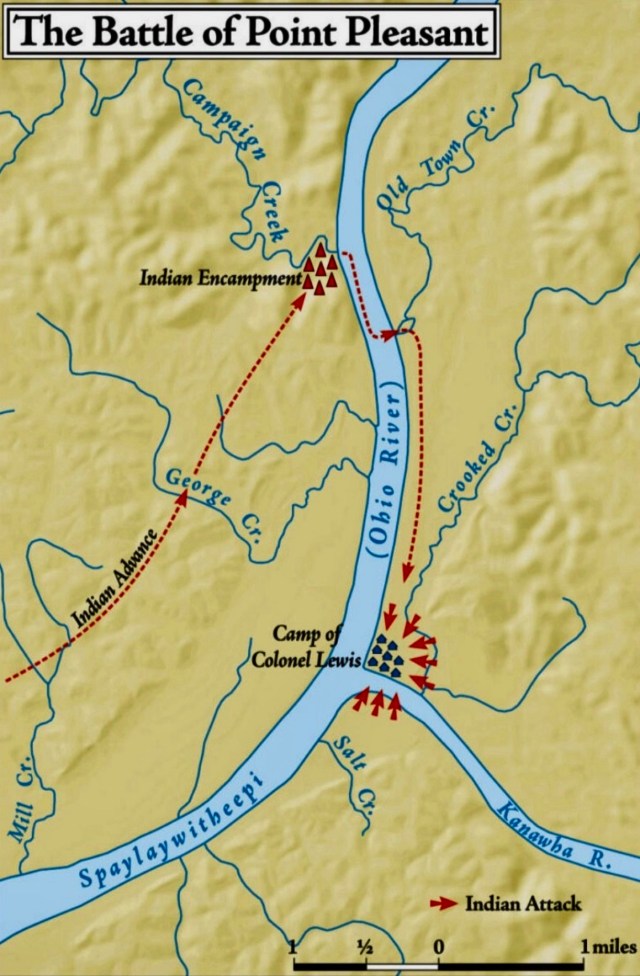
Under sustained fire, the militia detachments were finally able to link up. With their flanks no longer in the air, the battle line now stretched from the Ohio River over to Crooked Creek, making a flanking maneuver by the warriors next to impossible. John Field was killed; Evan Shelby took command of the entire line of battle. The fight had turned hand-to-hand. For several hours the bloody contest continued. Those Virginians who understood the Shawnee dialect afterwards claimed they had heard the sound of Cornstalk’s voice over the din of battle encouraging his warriors to “Fight and be strong”. Hand-to-hand combat, by its very nature, can be brutal and bloody. Both sides were suffering severe losses as the contest continued but Cornstalk made the decision to stay in the fight at Point Pleasant in order to inflict more damage to Lewis’ men. Withdrawing from the battle in order to fight another day put Cornstalk’s forces under a decided disadvantage. It would allow the wings of the Virginia militia to combine, closer to the Shawnee villages. He had to continue to fight as long as possible. But after so many hours, the allied warriors were beginning to falter, falling back under the pressure from the militia. The long rifles of the Virginians were now taking a heavy toll.

Col. Lewis sent orders to Capt. Shelby to advance his troops. With this surge, Cornstalk’s braves began to give more ground. Lewis earlier had ordered three companies of Augusta militia to move to the right, along the heights above Crooked Creek in order to flank the enemy. Now they opened fire, surprising the warriors on Cornstalk’s left. With knowledge that more militiamen were coming up from Camp Union, Cornstalk had no choice but to disengage at this point. Close to sunset, after hours of bloody combat, Cornstalk’s army began to withdraw, hoping to get back across the Ohio. They largely carried off their dead, throwing some of the bodies into the river to hide their losses. They were successful, however, and made the north bank of the river but Chief Cornstalk’s attempt to destroy the Southern Division had failed.
The Virginia militia had won the field, but at a terrible cost. Andrew Lewis lost around 75 men killed in the engagement with 140 more wounded. It’s believed that Cornstalk’s casualties were similar. Just before the battle, Lord Dunmore had moved his division inland, closer to the Shawnee villages, and established Camp Charlotte at Pickaway Plains. With his allied warriors not willing to engage further, Cornstalk had no choice but to initiate peace talks. His decision did, however, save the upper Shawnee towns from destruction.
With the subsequent Treaty of Camp Charlotte, Lord Dunmore’s War came to an end, but peace on the frontier would be fleeting. Within six months, shots were fired at Lexington and Concord, plunging America into war with Great Britain. More settlements were established in Kentucky and Shawnee raids would continue throughout the next twenty years.
With the coming of the American Revolution, Lord Dunmore himself would eventually be forced out of Virginia, pursued by some of the same militia officers he had commanded in the war that took his name.
For more about Point Pleasant and Dunmore’s War, check out our Rev War Revelry with Dr. Glenn Williams on our Facebook page or You Tube Channel.
Jefferson and Weedon
Emerging Revolutionary War welcomes back guest historian Michael Aubrecht
In 1777 Thomas Jefferson and a committee of revisors came to the City of Fredericksburg for the purpose of revising several Virginia statutes. This led to Jefferson drafting the Virginia Statute for Religious Freedom.
When Jefferson and his comrades arrived in Fredericksburg they were met with a town bristling with military activity. Troops were drilling in the public square and filled the crowded streets, buildings and shops. Awaiting travel orders were the men of the Second Virginia and the Seventh Virginia, ordered here on January 9 for a rendezvous just prior to marching to join General Washington at the front. By the time Jefferson arrived in Fredericksburg, sixty of the more than two hundred battles and skirmishes of the war had already taken place.
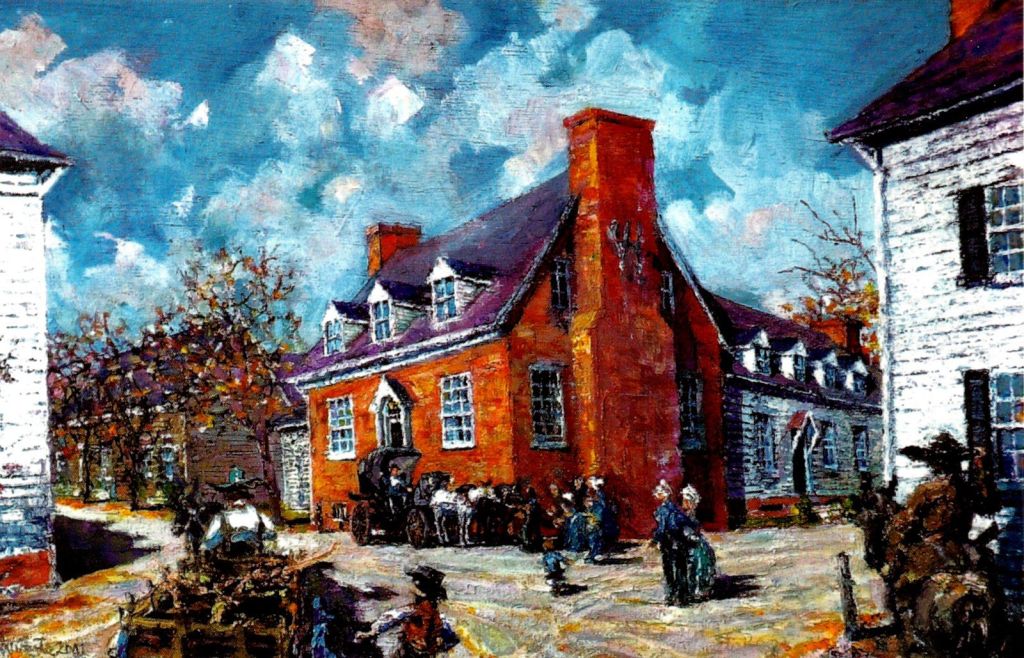


Visiting Historic Kenmore: A Preserved Patriot’s Home in Fredericksburg Virginia
Emerging Revolutionary War welcomes back guest historian Kate Bitely.
In the heart of Fredericksburg, Virginia, you will find a well-preserved, Georgian-style home that once belonged to Betty Washington Lewis, the sister of George Washington. Historic Kenmore, as the home is known today, was constructed in the 1770s and originally sat on 861 acres near downtown Fredericksburg. Today, the historic house museum is open for daily tours where guests can explore the gardens, the main living floor of the home, several historic structures on the priority, and a visitor center filled with riveting artifacts and information.
Nearly 290 years ago, Betty Washington was born at Pope’s Creek in Westmoreland County, Virginia. As a young child, she lived in a few properties owned by the Washington family before relocating to Ferry Farm, located in Stafford County, Virginia, where Betty, George and their siblings grew up. On February 22, 1750, Betty married Fielding Lewis, a widowed distant cousin, and a father of two young children. In 1752, the family purchased 1300 acres in the Fredericksburg area and allocated a portion of the land as the future site for their home Millbrook, which was eventually renamed to Kenmore in the 1800’s. In total, Betty and Fielding welcomed eleven children, but only six survived to adulthood.
Fielding Lewis was a well-known member of his community. He built his wealth initially as a merchant, but was later elected as a member of the House of Burgesses and served as a colonel in the Revolutionary War. During the war, however, Lewis used his finances to personally pay for munitions and supplies for Patriot troops which ultimately drained much of the family’s resources.
The Lewis family were staunch Patriots. In 1775, when the Lewis’s were moving into their home, the spirit of independence was strong throughout the colonies. Given the Washington’s status, heritage and devotion to service, Betty and her family would become one of the biggest supporters for the Patriot cause, willing to risk their home, finances, reputation, and their safety in favor of breaking away from England. The impressive residence served as a visual representation of their wealth, which became significantly more important during the Revolutionary War.
Continue reading “Visiting Historic Kenmore: A Preserved Patriot’s Home in Fredericksburg Virginia”Address from the Officers of the Virginia Regiment: December 31, 1758
Young George Washington’s performance in the French and Indian War is largely viewed as one of failure and recklessness. His actions in the Ohio River Valley ignited a conflict in North America that in turn lit the world ablaze. He could boast of no great military laurels, other than that he had emerged unscathed from the bloody battle of the Monongahela, and that he had commanded colonial provincials in Gen. John Forbes’ successful campaign against Fort Duquesne. He left military service following the latter event, with his hopes of receiving a commission in His Majesty’s Army worthy of his merit dashed years before.
However, one aspect of Washington’s service in the French and Indian War has been widely neglected. The commander of the Virginia Regiment was tasked with defending the western frontier from enemy raiding parties. It was an unenviable position that he tackled with limited resources. It was during this period that Washington began to develop the leadership qualities that would inspire others to follow him into the depths of Hell some twenty years later. On the last day of 1758, as Washington prepared to pursue a life outside of military greatness, the officers of the Virginia Regiment drew-up a heartfelt petition to urge the now 26 year-old colonel they had grown to admire to rescind his resignation. Below is that document:
“To George Washington Esqr. Collo. of the Virginia Regiment & Commander of all the Virginia Forces The humble Address of the Officers of the Virginia Regiment
Fort Loudoun, Dec. 31st 1758
Sir,
We your most obedient and affectionate Officers, beg Leave to express our great Concern, at the disagreeable News we h⟨ave received⟩ of your Determination to resign the Command of that Corps, in which we have under you long ⟨served⟩.
The ⟨happine⟩ss we have enjoy’d and the Honor we have acquir’d, together with the m⟨utua⟩l Regard that has always subsisted between you and your Off⟨icers,⟩ have implanted so sensible an Affection in the Minds of us all, that we cannot be silent at this critical Occasion.
In our earliest Infancy you took us under your Tuition, train’d us up in the Practice of that Discipline which alone can constitute good Troops, from ⟨the⟩ punctual Observance of which you never suffer’d the least Deviation.
Your steady adherance to impartial Justice, your quick Discernment and invarable Regard to Merit, wisely intended to inculcate those genuine Sentiments, of true Honor and Passion for Glory, from which the great military Atcheivements have been deriv’d, first heighten’d our natural Emulation, and our Desire to excel. How much we improv’d by those Regulations, and your own Example, with what Alacrity we have hitherto discharg’d our Duty, with what Chearfulness we have encounter’d the severest Toils, especially while under your particular Directions, we submit to yourself, and flatter ourselves, that we have in a great Measure answer’d your Expectations.
Judge then, how sensibly we must be Affected with the loss of such an excellent Commander, such a sincere Friend, and so affable a Companion. How rare is it to find those amiable Qualifications blended together in one Man? How great the Loss of such a Man? Adieu to that Superiority, which the Enemy have granted us over other Troops, and which even the Regulars and Provincials have done us the Honor publicly to acknowledge! Adieu to that strict Discipline and order, which you have always maintain’d! Adieu to that happy Union and Harmony, which has been our principal Cement!
It gives us an additional Sorrow, when we reflect, to find, our unhappy Country will receive a loss, no less irreparable, than ourselves. Where will it meet a Man so experienc’d in military Affairs? One so renown’d for Patriotism, Courage and Conduct? Who has so great knowledge of the Enemy we have to deal with? Who so well acquainted with their Situation & Strength? Who so much respected by the Soldiery? Who in short so able to support the military Character of Virginia?
Your approv’d Love to your King and Country, and your uncommon Perseverance in promoting the Honor and true Interest of the Service, convince us, that the most cogent Reasons only could induce you to quit it. Yet we with the greatest Deference, presume to entreat you to suspend those Thoughts for another Year, and to lead us on to assist in compleating the Glorious Work of extirpating our Enemies, towards which so considerable Advances have been already made. In you we place the most implicit Confidence. Your Presence only will cause a steady Firmness and Vigor to actuate in every Breast, despising the greatest Dangers, and thinking light of Toils and Hardships, while lead on by the Man we know and Love.
But if we must be so unhappy as to part, if the Exigencies of your Affairs force you to abandon Us, we beg it as our last Request that you will recommend some Person most capable to command, whose Military Knowledge, whose Honor, whose Conduct, and whose disinterested Principles we may depend upon.
Frankness, Sincerity, and a certain Openness of Soul, are the true Characteristics of an Officer, and we flatter ourselves that you do not think us capable of saying anything, contrary to the purest Dictates of our Minds. Fully persuaded of this, we beg Leave to assure you, that as you have hitherto been the actuating Soul of the whole Corps, we shall at all times pay the most invariable regard to your Will and Pleasure, and will always be happy to demonstrate by our Actions, with how much Respect and Esteem we are, Sir, Your most affectionate & most obedt humble Servants.”[i]
[i] “Address from the Officers of the Virginia Regiment, 31 December 1758,” Founders Online, National Archives, https://founders.archives.gov/documents/Washington/02-06-02-0147. [Original source: The Papers of George Washington, Colonial Series, vol. 6, 4 September 1758 – 26 December 1760, ed. W. W. Abbot. Charlottesville: University Press of Virginia, 1988, pp. 178–181.]
Americana Corner

Emerging Revolutionary War checks in with Tom Hand and Americana Corner. Here is what has has been published on that blog for the month of July.
Ben Franklin Enters Politics
July 26, 2022
Benjamin Franklin retired from an active role in his printing business in 1748 at the age of 42. His work had made him a wealthy man, and he decided to devote the remainder of his life to civic improvements and governmental affairs. Franklin became a member of the Philadelphia City Council that same year, beginning a period of more than four decades of involvement in American politics and statecraft.
Virginia’s House of Burgesses, British America’s First Elected Legislature
July 19, 2022
The Colony of Virginia was established at Jamestown by the Virginia Company in 1607 as a for-profit venture by its investors. To bring order to the province, Governor George Yeardley created a one-house or unicameral General Assembly on July 30, 1619.
How Colonial America Was Governed
July 12, 2022
When the English began to settle North America in the 1600’s, the leaders of the various colonies had different motives. While all colonies exercised their authority in the King’s name, they were not created in the same mold, and some had more autonomy than others. In fact, there were three different types of colonies: royal, self-governing, and proprietary.
Ben Franklin, America’s First Man of Science
July 5, 2022
Benjamin Franklin was one of the world’s foremost inventors and scientists in the 1700s. His creative genius and inventiveness led to many significant discoveries that made living life easier for all. Moreover, he was proof positive that brilliant minds existed in British America, despite its backwoods reputation in Europe.



