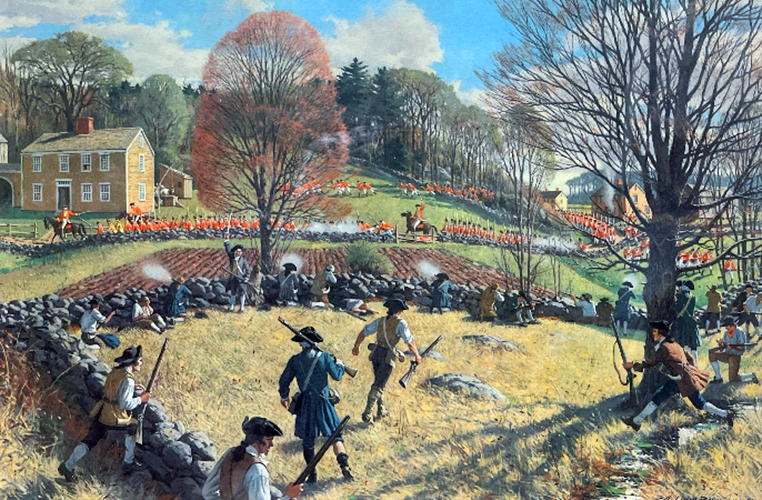After years of political unrest between Great Britain and her North American colonies, tension finally boiled over into armed conflict on April 19, 1775, at Lexington and Concord. The British expedition to capture arms and munitions held by the colonists at Concord disintegrated into a panic-ridden retreat to Boston as local militias struck the column as it moved through the Massachusetts countryside. As often happens in war, seeds planted during a battle often sow the next.
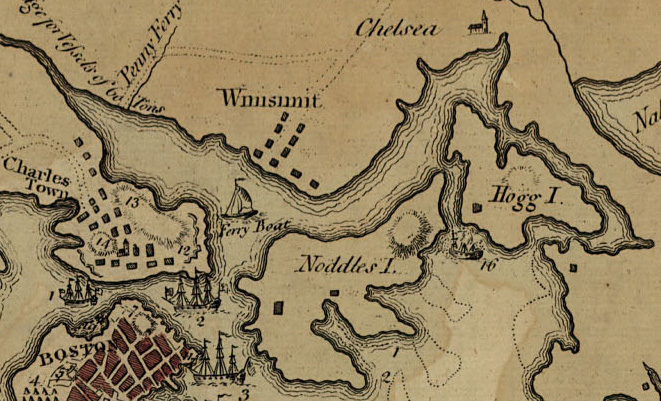
Rather than enter march through Boston Neck British officers diverted to Cambridge and proceeded to the Charlestown Peninsula. Bordered by the Charles and Mystic Rivers, the peninsula jutted out into Boston Harbor northeast of the city. As darkness settled in, exhausted British soldiers made their way onto 110-foot high Bunker Hill. This eminence, commanded Charlestown Neck, a narrow sliver of land connecting to the mainland, along with the surrounding landscape.
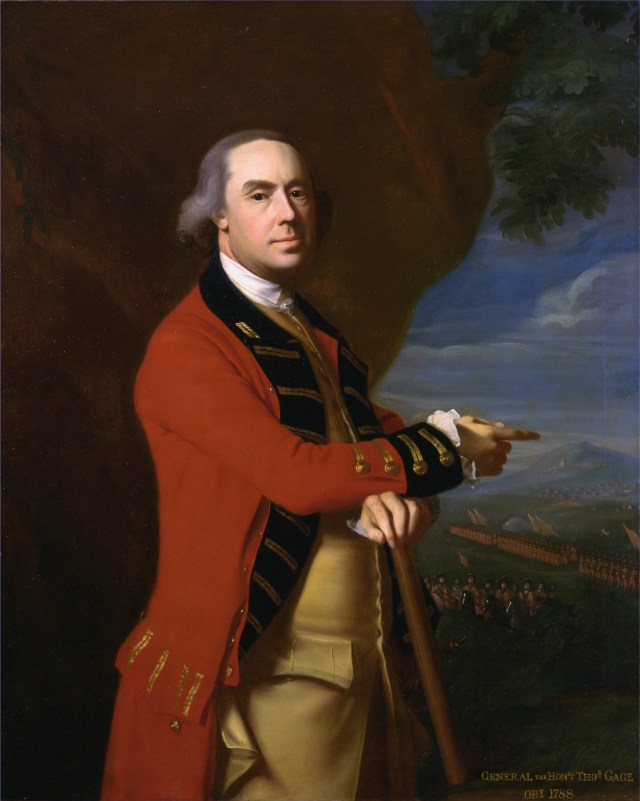
That night, Lt. Gen. Thomas Gage, the British Commander-in-Chief met with Vice Admiral Samuel Graves, head of the North Atlantic Squadron. Among other suggestions, Graves urged Gage to burn Charlestown and occupy Bunker Hill. Graves likely knew that his ships in the harbor could not elevate their artillery to reach the high ground. Additionally, Bunker Hill was out of range of the Copp’s Hill Battery located in the city’s North End.
Gage recognized the long-simmering pot would eventually boil over with the colonists. “If you think ten thousand men sufficient, send twenty; if one million thought enough, give two; you save both blood and treasure in the end,” he wrote the previous fall to his superiors in London. Now, seemingly distant from the tactical situation on the ground, the survivor of the Monogahela rejected Graves’ proposal, claiming “the weakness of the army.” One must wonder if this was a decision Gage came to privately regret.
The arrival of reinforcements at the end of May, along with Maj. Gens. John Burgoyne, Henry Clinton, and William Howe may have buoyed Gage’s spirits. He soon began making plans to break out of Boston. In consultation with his subordinates, Gage formulated a plan to strike first across Boston Neck to capture Dorchester Heights, which commanded the southern end of the city. A second attack would capture Charlestown then move the three miles to Cambridge to hopefully destroy the Massachusetts army. The offensive was slated to take place on June 18.
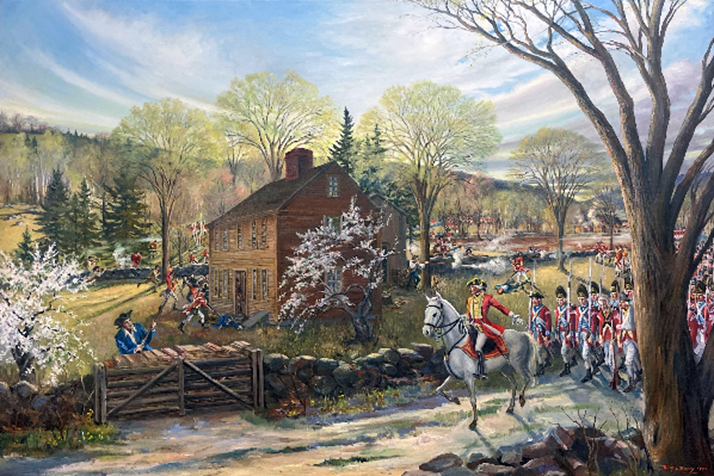
Read more: British Leadership – Bunker HillUnfortunately, Boston leaked like a sieve and Gage failed to maintain what is known today as operational security. His plans were soon known in Cambridge where the Massachusetts Committee of Safety authorized their own effort to occupy Bunker Hill ahead of the British. On the night of June 16, colonial units led by Col. William Prescott marched out of Cambridge toward Charlestown. Rather than follow his orders, Prescott moved to the 60 foot high Breed’s Hill, located slightly to the southeast of Bunker Hill. Prescott’s decision remains one of the great mysteries surrounding the battle. His men began construction of a redoubt.
Another question surrounding the engagement rests with Henry Clinton. Sometime on the evening of June 16, Clinton wrote he conducted a reconnaissance and claimed he witnessed Provincial activity. He did not, however, explain where he went nor reported the type of actions he saw. Additionally, visibility would be difficult in the growing dusk. Clinton further stated he reported his findings to Gage and Howe but Gage elected to wait for daylight.
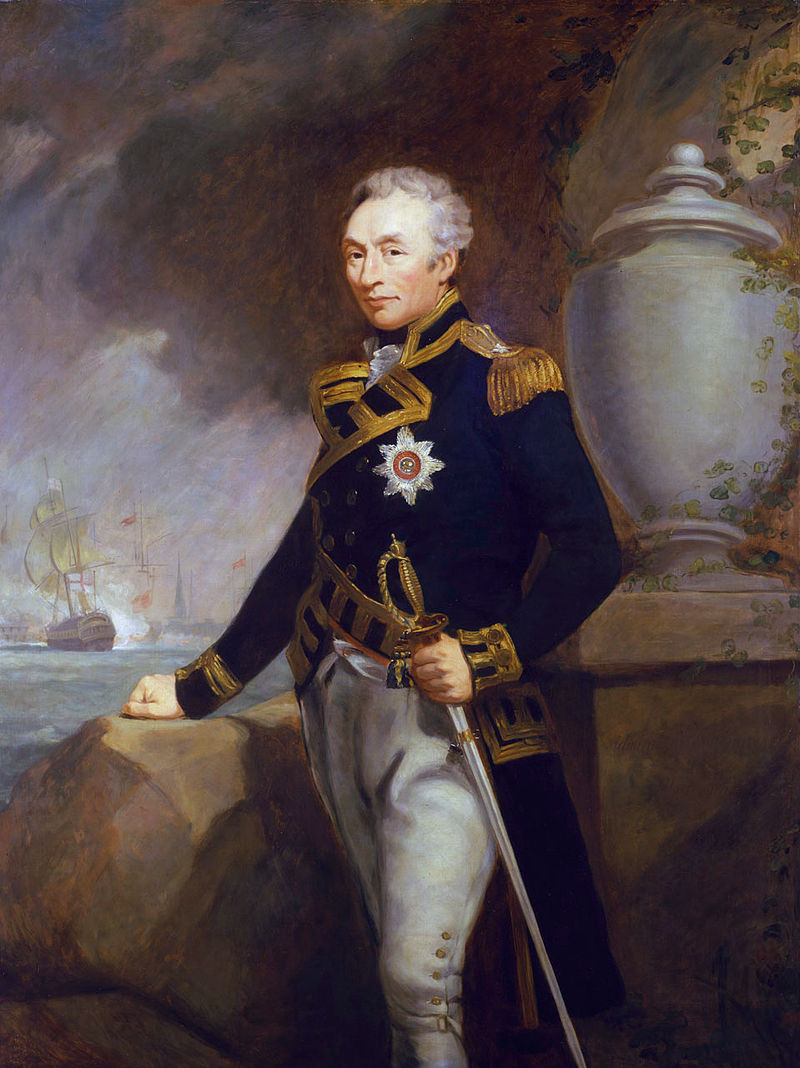
Sunrise revealed Prescott’s men atop Breed’s Hill, hard at work on the redoubt, which threatened the northern end of the city. Gage and his officers quickly convened at his headquarters at the Province House. Howe, the senior officer, would be in command. Some thought was given to sail up the Mystic to land on Charlestown Neck well in the rear of the redoubt. This plan was quickly nixed for fear the force could be isolated and cut off by reinforcements from Cambridge and militia on Breed’s Hill. It was eventually decided Howe would land below and out of range of the redoubt. Orders soon went out for the mustering of the “ten oldest companies” the flank and grenadiers, each – along with several regiments to prepare for the operation.
Each British regiment consisted of ten companies, eight line, with two flank and grenadier companies. The flank companies consisted of men who were often the shortest and fastest, who could operate in open order tactics, moving quickly to engage and skirmish with the enemy. The grenadiers, identified by their bear skin hats, were often the tallest men in the regiment and were used as the shock troops during an attack. By the time of the American Revolution, they were no longer carrying hand grenades but the name remained. Oftentimes these companies were separated from their regiments and placed in their own battalions.
Howe disembarked from Long Wharf, going over himself in the second wave, that afternoon. The British landed at Moulton’s Hill, near the modern Navy Yard. Stepping ashore, Howe observed his objective. “On first view it was clearly seen that the rebels were in forced and strongly entrenched upon their right in the Redoubt that had been seen from the town at daybreak,” he reported. “Their left and center were covered by a breastwork which reached from the Redoubt to the Mystick, the space from the Redoubt to that river being about 380 yards, and the whole extent they occupied about 600 yards”. The extent of the defenses compelled Howe to call for reinforcements.
Toward the middle of the day, the British launched their assault. Although Howe’s second in command, Brig. Gen. Robert Pigot was present and directed the left of the line, Howe also decided to take a stronger role and led the center himself on foot. Howe directed his light infantry to advance along the beach of the Mystic, likely with the hope in mind of getting behind the redoubt. This attack was met and repulsed by New Hampshire militia under Col. John Stark. So too were Howe’s and Pigot’s attacks. Watching his men come stumbling back after the failed attempt prompted Howe to later write “it was a moment I had not felt before.”
In the second assault, Howe attempted to further squeeze off the redoubt, pulling the light infantry from the beach to augment his center. At the same time, Pigot sent the 1st Marine Battalion and the 47th Regiment of Foot to get between Charlestown and the redoubt. During the assault, which also failed, the light infantry fired into the rear of the grenadiers, inflicting casualties.
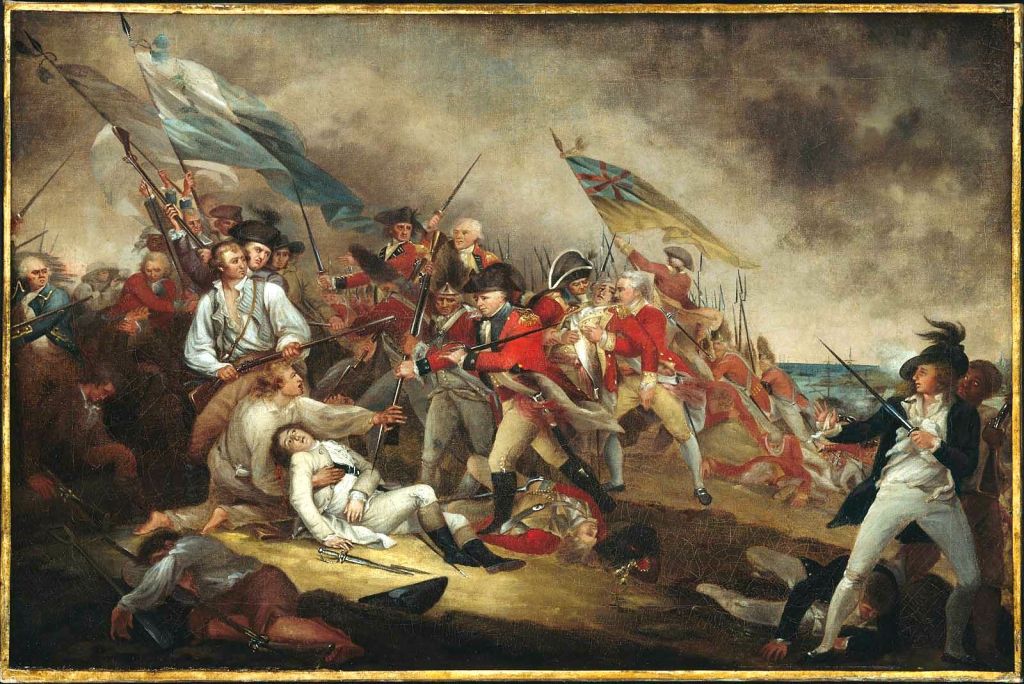
Once again, the British lurched forward, determined to overwhelm the redoubt by a sheer force of numbers. This time, luck was with them as the militia were running out of ammunition. Francis, Lord Rawdon, an officer in the 5th Regiment of Foot who would go on to distinguish himself in the Southern Campaigns recalled “our men grew impatient, and all crying Push on, Push on, advanced with infinite spirit to attack the work with their small arms. As soon as the rebels perceived this, they rose up and poured in so heavy a fire upon us that the oldest officers say they never saw a sharper action. They kept up this fire until we were within ten yards of them…there are few instances of regular troops defending a redoubt till the enemy were in the very ditch of it.”
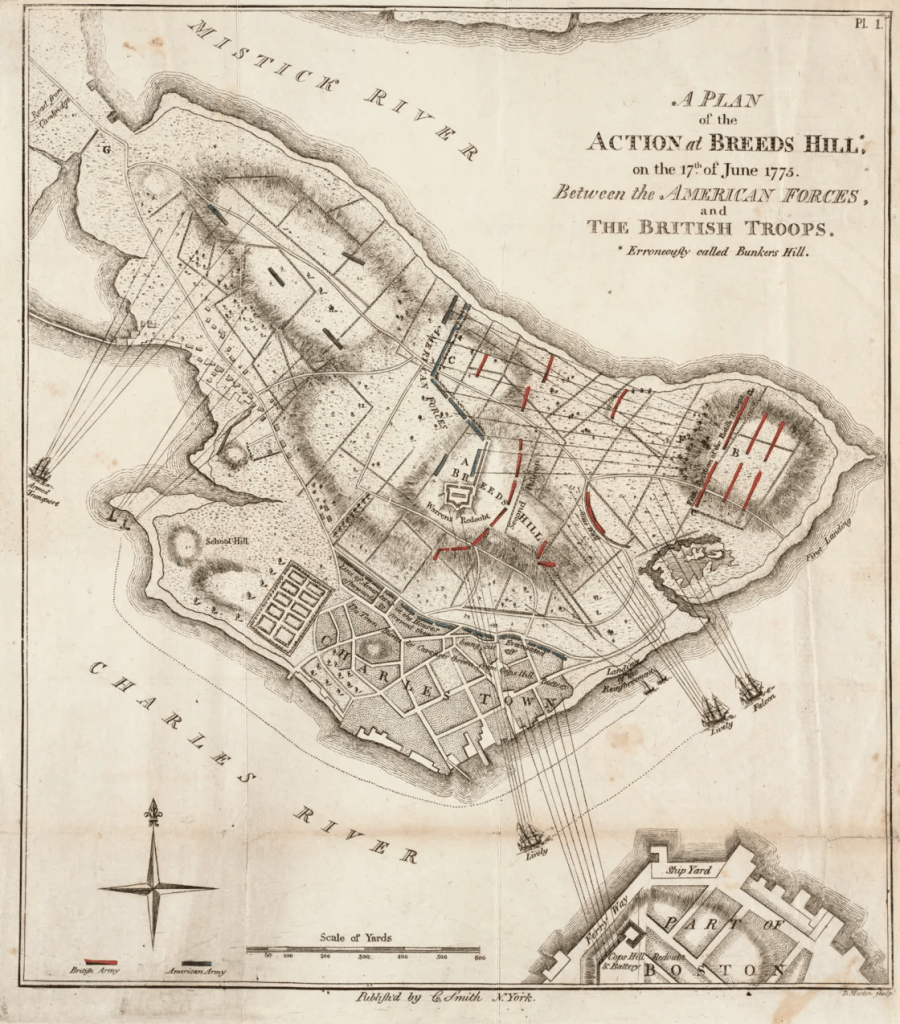
The British infantry swarmed into Prescott’s redoubt. Somewhere in the maelstrom was British lieutenant and adjutant of the 1st Marines, John Waller. “Nothing could be more shocking than the carnage that followed the storming of this work,” he wrote “We tumbled over the dead to get at the living who were crowding out of the gorge of the redoubt…’twas streaming with blood and strewed with the dead and dying men, the soldiers stabbing some and dashing out the brains of the others.” The colonials managed to retreat across Charlestown Neck, the British too exhausted to give chase.
Bunker Hill became the first of many pyrrhic victories for the British over the course of the American Revolution. Still, there were a number of shortcomings. Howe, rather than oversee the attacks from Moulton’s Hill, led the assaults himself. Perhaps he needed to inspire his men or he recognized the importance of the situation but he reverted to being a battalion commander. One must wonder whether the initial attacks could have been more effective had he delegated authority and used more of a guiding hand. Howe’s experience that day may have influenced him for the remainder of the war. Rather than rely on frontal assaults, he utilized flanking maneuvers such as those at Long Island and Brandywine. The friendly fire casualties can be attributed to inexperience amongst the ranks. Gage, along with his subordinates also share, the blame for not maintaining operational security and letting their plans slip out of Boston. Additionally, Gage failed to heed the advice of Graves and secure Charlestown Peninsula in April when he had the opportunity. The result nearly two months to the day resulted in over 1,000 British soldiers killed and wounded, a high cost of blood and treasure, in a war that would lead to the independence of the United States.